This is a talk presented at DETERMINISTIC AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES conference held at the Apollonia University Iasi together with the Romanian Acadmy of Science (Iasi branch), Feb 25-28 2026.
Talk materials: ![]() the slides of the presentation.
the slides of the presentation.
personal page
Teacher: Gabriel TURINICI
Content
Historical note: 2019/21 course name: « Approches déterministes et stochastiques pour la valuation d’options » + .
Instructor: Gabriel TURINICI
1/ Introduction to reinforcement learning
2/ Theoretical formalism: Markov decision processes (MDP), value function ( Belman and Hamilton- Jacobi – Bellman equations) etc.
3/ Common strategies, building from the example of « multi-armed bandit »
4/ Strategies in deep learning: Q-learning and DQN
5/ Strategies in deep learning: SARSA and variants
6/ Strategies in deep learning: Actor-Critic and variants
7/ During the course: various Python and gym/gymnasium implementations
8/ Perspectives.
 Principal document for the theoretical presentations: (no distribution autoried without WRITTEN consent from the author) (see « teams » group for updated version)
Principal document for the theoretical presentations: (no distribution autoried without WRITTEN consent from the author) (see « teams » group for updated version)
Multi Armed Bandit codes (MAB) : play MAB, solve MAB , solve MAB v2., policy grad from chatGPT to correct., policy grad corrected.
Bellman iterations: code to correct here, solution code here
Gym: play Frozen Lake (v2023) (version 2022)
Q-Learning : with Frozen Lake: version to correct here. Full versions: python version or notebook version
-play with gym/Atari-Breakout: python version or notebook version
Value function iterations (Belmman) on FrozenLake : version to correct here
Deep Q Learning (DQN) : Learn with gym/Atari-Breakout: notebook 2024 and its version with smaller NN and play with result
Policy gradients on Pong adapted from Karpathy, 2024 version (correct to get it working!) python or notebook
You can also load from HERE a converged version (rename as necessary) pg_pong_converged_turinici24
Notebook to use it: here (please send me yours if mean reward above 15!).
Some links: parking human, parking AI
Projets : cf. Teams
Instructor: Gabriel TURINICI
Preamble: this course is just but an introduction, in a limited amount of time, to Statistical and Machine learning. This will prepare for the next year’s courses (some of them on my www page cf. « Deep Learning » and « Reinforcement Learning »).
Course outline
1/ Examples and machine learning framework
2/ Useful theoretical objects: predictors, loss functions, bias, variance
3/ K-nearest neighbors (k-NN) and the « curse of the dimensionality »
4/ Linear and logistic models in high dimension, variable selection and model regularization (ridge, lasso)
5/ Stochastic Optimization Algorithms
6/ Naive Bayesian classification
7/ Neural networks : introduction, operator, datasets, training, examples, implementations
8/ K-means clustering
Reference:

 Exercices, implementations, current course textbook (no distribution autorized without WRITTEN consent from the author): see « teams » group.
Exercices, implementations, current course textbook (no distribution autorized without WRITTEN consent from the author): see « teams » group.
In a recent interview with Mathilde Texier from France Televisions we discuss how video deepfakes mixes with societal and political news to generate misinformation.
Teacher: Gabriel TURINICI
Summary:
1/ Deep learning : major applications, references, culture
2/ Types: supervised, renforcement, unsupervised
3/ Neural networks: main objects: neurons, operations, loss fonction, optimization, architecture
4/ Stochastic optimization algorithms and convergence proof for SGD
5/ Gradient computation by « back-propagation »
6/ Pure Python implementation of a fully connected sequential network
7/ Convolutional networks (CNN) : filters, layers, architectures.
8/ Pytorch and Tensorflow(Keras) implementation of a CNN.
9/ Techniques: regularization, hyper-parameters, particular networks, recurrent (RNN, LSTM);
10/ Unsupervised Deep learning: generative AI, GAN, VAE, Stable diffusion.
11/ Keras VAE implementation. “Hugginface” Stable Diffusion.
(12/ If time allows: LLM & NLP: word2vec, Glove (exemples : woman-man + king = queen)
| Documents | ||
 MAIN document (theory): see your teams channel MAIN document (theory): see your teams channel(no distribution is authorized without WRITTEN consent from the author) |  for back-propagation for back-propagation | SGD convergence proof |
| Implementations |
| Function approximation by NN : notebook version, Python version Results (approximation & convergence) 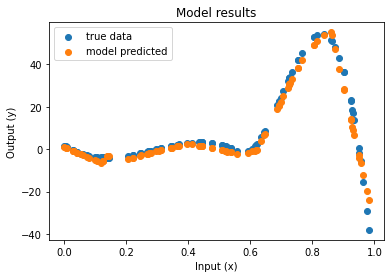 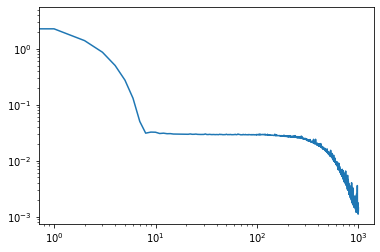 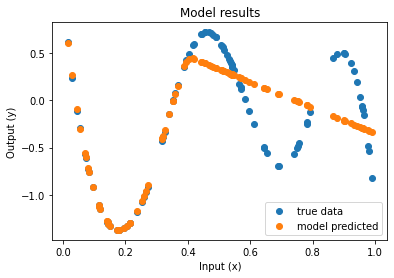 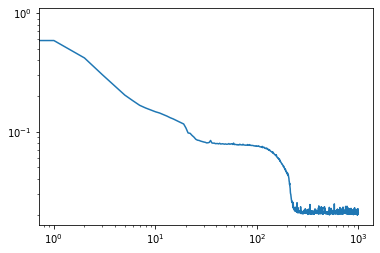 After 5 times more epochs 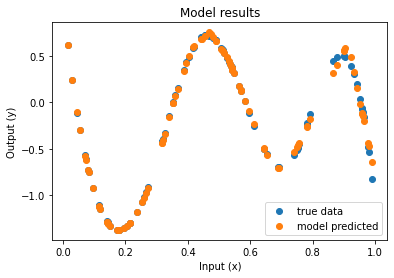 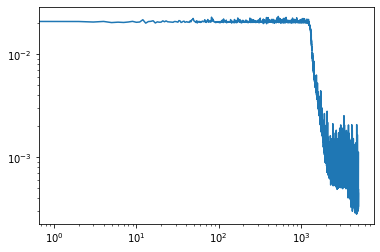 Official code reference https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7220367 |
| Pure python (no keras, no tensorflow, no Pytorch) implementation (cf. also theoretical doc): – version « to implement » (with Dense/FC layers) (bd=iris), – version : solution If needed: iris dataset here Implementation : keras/Iris , pytorch (tensorflow) CNN example: https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/images/cnn Pytorch example CNN/MNIST : python and notebook versions. Todo : use on MNIST, try to obtain high accuracy on MNIST, CIFAR10. |
| VAE: latent space visualisation : CVAE – python (rename *.py) , CVAE ipynb version |
| Stable diffusion: Working example jan 2025: python version, Notebook version Old working example 19/1/2024 on Google collab: version : notebook, (here python, rename *.py). ATTENTION the run takes 10 minutes (first time) then is somehow faster (just change the prompt text).  |
This is a talk presented at Nanmat conference held Nov 3-6 2026 at ICTP, Cluj.
Talk materials: ![]() the slides of the presentation. and here the
the slides of the presentation. and here the  Youtube video version.
Youtube video version.
Took part recently at a round table on AI in medecine within the AI4-MED conference. Several subjects were touched including the concerns, the safeguards, the trust in complex situations. More detailed reproduction of the discussion will follow on another outlet.
During the FAAI 2025 conference I presented a recent work with Pierre Brugière on . See here the paper (arxiv version) and here the slides.
Executive summary: we introduce a deep-learning framework for hedging derivatives in markets with discrete trading and transaction costs, without assuming a specific stochastic model for the underlying asset. Unlike traditional approaches such as the Black–Scholes or Leland models, which rely on strong modeling assumptions and continuous-time approximations, the proposed method learns effective hedging strategies directly from data. A key contribution is its ability to perform well with very limited training data—using as few as 256 simulated price trajectories—while outperforming classical hedging schemes in numerical experiments under a geometric Brownian motion setting. This makes the approach both robust and practical for real-world applications where data and model certainty are limited.
In a recent interview with Alexandre Boero from Clubic we discuss how recent technologies rendered possible a growing network of fake online media sites and journalists entirely generated by AI, designed to appear credible and manipulate audiences and advertisers, raising serious concerns about misinformation and the erosion of trust in digital content.