M1 mathématiques appliquées, Université Paris Dauphine -PSL, 2019-2020
Responsable: Gabriel TURINICI
Contenu
1 Introduction et rappels
2 Estimation de la fonction de répartition
3 Tests robustes
4 Estimation de densités par estimateurs à noyau
5 Régression non paramétrique
Bibliographie: poly distribué
Documents de support de cours, autres documents
NOTA BENE: Tous des documents sont soumis au droit d’auteur, et ne peuvent pas être distribués sauf accord préalable ECRIT de l’auteur.
Supports de cours
poly distribué, attention il s’agit d’une version mise à jour au fur et à mesure (dernière mise à jour 26/3/20).
Notes du cours : poly annoté cours 1et 2 (lien ancien, ne pas utiliser) , cours 3 , cours 3,4 notes manuscrites
feuilles de TD: TD1,
corrigé ex 2018: regarder l’exo 3 qui demontre le fait que la convergence des cdf en tout point de continuite est pareil que celle de l’inverse généralisée.
Nouveau (6/5/2020): version poly avec les TD3,TD4
Séances de cours en non-présentiel
(confinement printemps 2020)
Cours
Séance prévue le 27 mars 2020: vidéo youtube ICI
Sinon: utiliser le poly du cours usuel, les notes manuscrites et annotations ci-dessus.
Séance prévue le 2 avril 2020: vidéos youtube ICI (2 vidéos) :
Test de Wilcoxon,
propriétés des rangs.
Séance prévue le 3 avril 2020: vidéos youtube ICI (2 vidéos) :
Test de Mann-Whitney partie 1/2
Test de Mann-Whitney partie 2/2
Séance prévue le 24 avril 2020: vidéo youtube ICI (1 vidéo):
Estimation de densité partie 1/1
Séance prévue le 30 avril 2020: début de séance = consultation de la vidéo:
Estimation de densité par estimateurs à noyau
Ensuite : questions reunion « teams ».
Séance prévue le 7 mai 2020: début de séance = consultation de la vidéo:régression non paramétrique
Ensuite : questions reunion « teams ».
Séance prévue le 15 mai 2020: début de séance = consultation des vidéos: régression non paramétrique par polynomes locaux, ET régression: validation croisée et phénomène d’overfit,
Ensuite : questions reunion « teams ».
EXAMEN
Examen le 28/5 2020 à 14H00 (1H d’examen): conectez vous sur MYCOURSE. Il s’agit d’un QCM à remplir en ligne (PAS d’envoi par email, il ne sera pas noté).
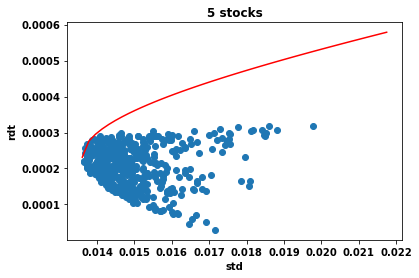
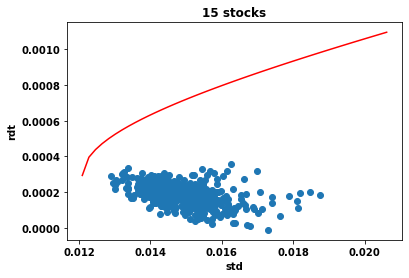
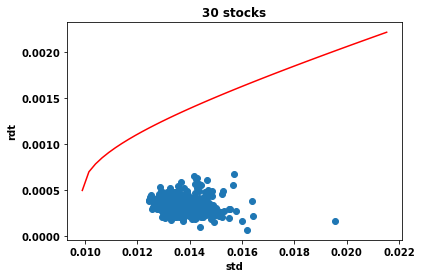
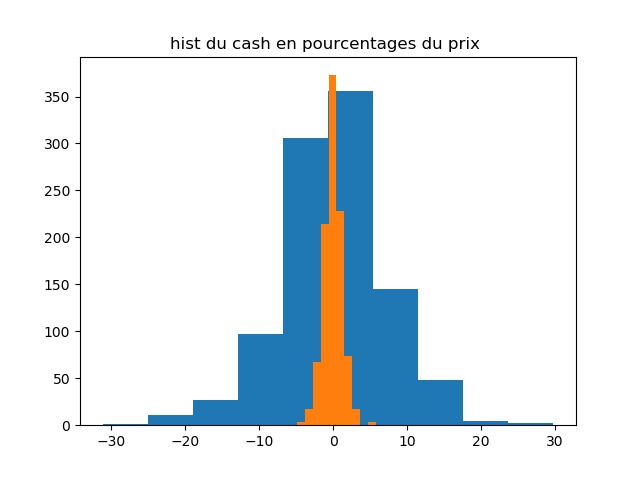


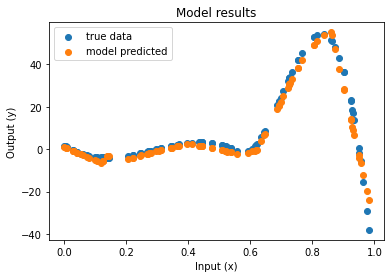
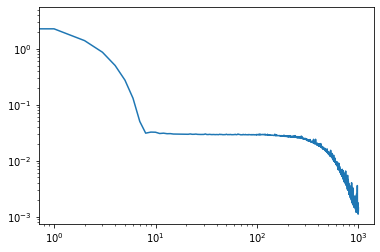
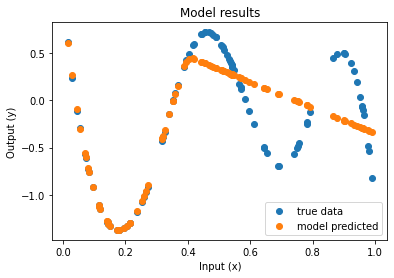
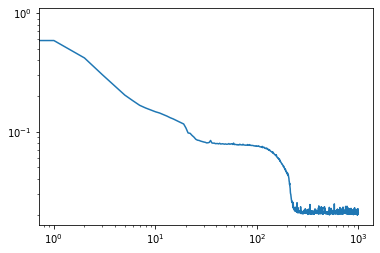

 Cours 1 : sections 1.1-1.2
Cours 1 : sections 1.1-1.2 




